In badminton and tennis, global participation is growing steadily. In 2021, the value of their market size was USD 10706.33 million, and within one year, it grew to USD 11362.63 million.
There could be multiple reasons, but one is that their service rules are interesting for audiences. I remained strictly on your query about “services of both games” throughout the blog.
First, I tried to briefly explain important terminologies of both games that can be helpful for totally new persons to these games, and if you already know them, then directly go to the outline “Comparison and contrast in service rules of Badminton and tennis” using “table of contents”.
Important Terminologies Used in Badminton & Tennis
There are many terminologies used in both games, but I mentioned only those that are related to service in both games for easy understanding of the comparison.
“Service” in Badminton and Tennis
Service is the action of the player. When the player hits a shuttlecock or ball, it is called service. The goal of the player is to ensure that it travels and lands in the opponent’s service court.
“Rally” in Badminton and Tennis
A Rally is a sequence of shots where the shuttlecock or ball is hit back and forth between opposing players or teams. The rally begins with service, and it ends when a shuttlecock or ball hits the ground.
“Service Box” in Badminton and Tennis
Service Box is a specific area in the court. It is the place where the player must stand to start the game.
“Let Service” in Tennis
When a served ball touches the net but still lands in the proper search box, it is called Let service. In this case, the server takes another shot without any penalty.
“Double Fault” in tennis
When a player makes two consecutive errors, as a result, the ball does not land in the proper search box. It is called Double Fault. That player loses a point.
“Deuce” in tennis
When both players or teams have won three points each in a game, a Deuce occurs. Then, a player or team wins when they make two consecutive points.
“Advantage in, Advantage out” in Tennis
In Deuce, if a player or team (server) wins one point, then that player or team has an Advantage. If the receiver player or team wins the point after the deuce, then they have an Advantage. So it needs one more point to win.
The Service Rules in Badminton

- The winner of the toss chooses to serve first or which side of the court he wants.
- The server stands on the right side of the service court.
- When he strikes the shuttlecock, both his feet must contact the floor.
- The server and receiver must stand diagonally on opposite sides
- They should not touch the boundaries of the court
- Players can switch sides when the point is won ‘on serve’ in doubles.
- The player serves underarm to the service box.
- Players’ feet must be stationary until the serve is made.
- The team that wins the rally serves first in the next rally.
- Players change sides after each point.
- A match is played best out of three games.
- Each game is played with 21 points.
- The player wins points when the opponent commits faults.
- Faults are shuttlecock landing outside of boundaries, a player’s foot crossing the boundary, fault serve, double hits in one turn, player touching the net, in doubles, moving the receiver his feet before serve, and invading the opponent’s court.
- Last and most common, a player who wins a rally adds a point to his side.
The Service Rules in Tennis
- Who serves first is determined by the coin toss winning.
- If the server is on the right side of the court, he must deliver the ball in the left side service box and vice versa.
- After making each point, players have 25 seconds to prepare for the next serve.
- If a player fails to deliver the ball into the service box, it counts as a fault.
- If a player steps on or over the baseline, it is also a fault.
- Point losses when two consecutive faults are committed.
- After letting service, the receiver gets another chance to serve without penalty.
- Servers can switch sides after each point.
- Double faults result in the loss of a point.
- Points are awarded as 15, 30, 40.
- The first point is 15 scores, the second is 30 scores, and the third is 40 scores.
- Winning a fourth point is the win of a game.
- If both players have 40 scores, then a player must win a point from “advantage in or advantage out”.
- The player won the set when he won at least six games.
- If the set is with a 6-6 tie, a tiebreaker is played.
- The player who wins the best of five sets wins the match.
- A female player needs to win two out of three sets, to win the match.
Comparison Between Service Rules of Badminton and Tennis
Badminton and tennis are played with rackets, but there are many differences between them.
Badminton
- Correct service is when the shuttlecock is delivered to the opponent’s side without touching the net.
- The server must stand in the right service court.
- The receiver must stand on the opposite side.
- Both players must not touch boundaries during the serve.
- The game points limit is 21.
- The match win is the best out of the three.
- The shuttlecock must not touch the ground.
- A player must not hint at the shuttlecock more than once in his turn.
- While striking the shuttlecock, both his feet must contact the floor.
- Faults are shuttlecock landing outside of boundaries, a player’s foot crossing the boundary, fault serve, double hits in one turn, player touching the net, in doubles, moving the receiver his feet before serve, and invading the opponent’s court.
Tennis
- Let service is if the ball touches the net but lands in the correct service box. It does not result in a point loss.
- It involves serving a ball into the diagonally opposite service box.
- Always during the game.
- Not necessary
- Points are awarded as 15, 30, 40.
- The match win is the best out of five sets.
- The ball can bounce once or twice before being played.
- Not apply to tennis
- Not essential in tennis
- Faults are service fault, foot fault, double fault, and let service.
Badminton Court Dimensions
A badminton court is a rectangular surface used for racket sports. The area is divided in half by the net. The badminton court has a length of 13.4 m. The badminton court’s width for doubles play is 6.1 m, but for singles play, it is 5.18 m.
Badminton Court Lines
There are a total of thirteen lines in the badminton court. There are 5 pairs of lines. Each pair contains two lines. Two lines are in a row that differentiates the service court, and one line is under the net that divides the service court in half.
Names of the Service Lines
To better understand the lines, here are the names. You can look at the picture for a better view:
- Long service line
- Short service line
- Badminton’s net line
- Sidelines
- Centre line
Badminton Line Dimensions
Knowing about the dimensions is important according to BWF. It gives you an insight into how much space you have to move. The covered area should be rectangular and covered with 40 mm wide lines. Color the lines with yellow or white paint to make them visible.
Here are the dimensions:
- The length of short lines is 17 feet
- The length of the long service line is 20 feet
- The length of the sideline is 43.9 feet
- The length of the badminton net line is 20 feet
- The length of the centre line is 12.7 feet
Lawn Tennis Net Measurement
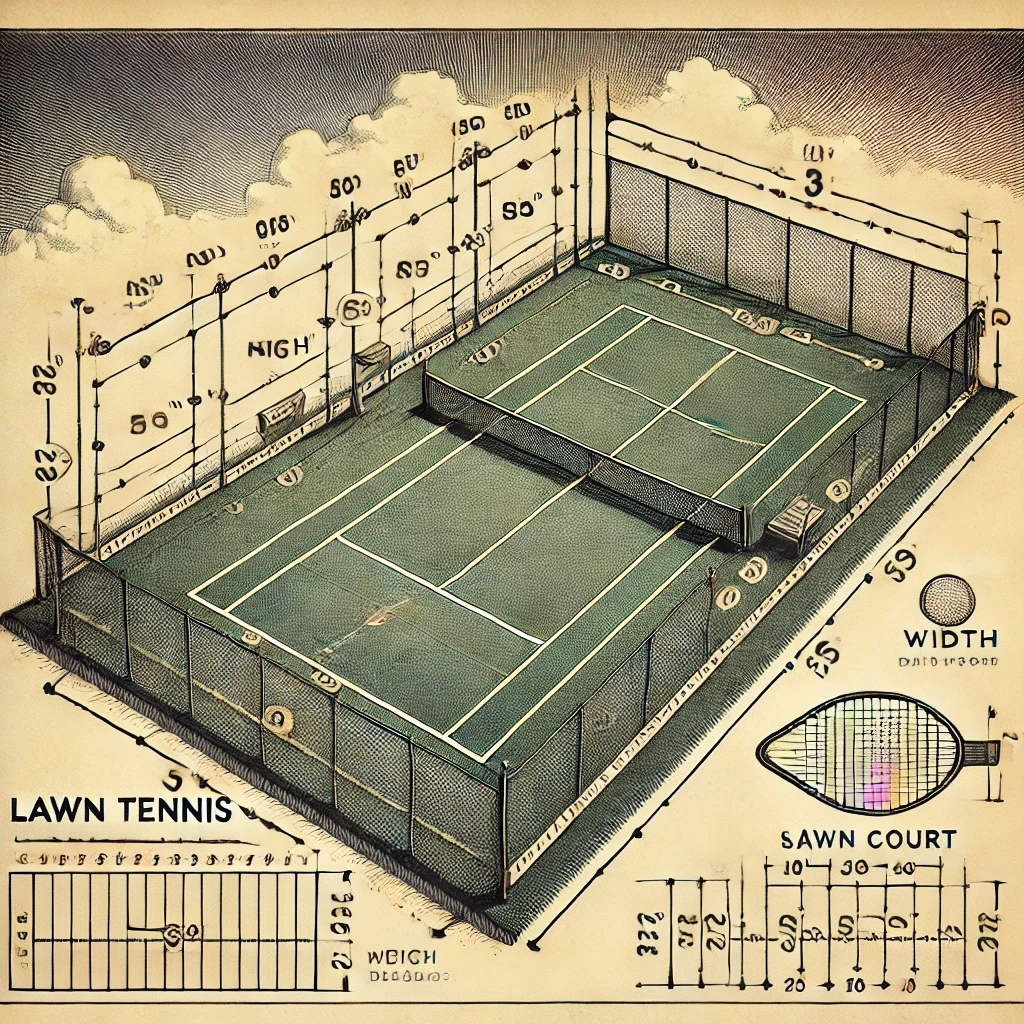
Here are the details of lawn tennis measurement:
Net width
The tennis net width for single matches is 36 feet, and for double matches, it is reduced to 33 feet.
Net Height
The height of the net should be 3.5 feet. From the centre, the net is sagy due to the material load. In the centre, the net will be 3 feet high.
Mesh Size
The mesh size of the net should not be more than 2.5 Square inches so the ball cannot pass through.
Material
The tennis is made of braided net cord material, which is durable and good for use in rain, especially for lawn tennis.
4 Types of Serve in Badminton
Here are the four types of serve in badminton:
High Serve
This serve is mostly used in single play. This serve allows them to push the opponent at the back of the line, making it difficult to make a strong comeback.
Execution
The shuttle is hit from the line to gain more height and depth. This makes the shuttle ideally landing close to the back line.
Low Serve
This serve is common in both single and double games. This allows the shuttle to skim near the net in front service lines by making a shallow return.
Execution
The shuttle is hit with a soft touch that makes it barely cross the net, preventing the opponent from making an aggressive return.
Flick Serve
This is the deceptive serve used in doubles. This serve catches the opponent off guard. He thinks the serve is low and just the aim of the shuttle at the back lines.
Execution
This serve is similar to a low serve, just with a wrist flip that sends the shuttle to the back end. This way, you can check the speed and timing of the opponent.
Drive Serve
This serve is least used in both single and double play, but it is effective. It has an element of surprise by increasing speed to force the opponent to make a weak return.
Execution
The shuttle is hit flat and fast. The shuttle travels horizontally at speed, just crossing the net.
Badminton Racket Dimensions
Here are the dimensions of a badminton racket:
Overall Length
The overall length of the racket from the head to the bottom cannot exceed 26.77 inches.
Width
The width of the racket normally measures the wide part of the head, which cannot be more than 9.06 inches.
Weight
The rackets are generally lightweight. The weight can vary from 70 to 95 grams without strings. The range of rackets available for 2U racket weight varies from 90 to 94g, and racket of 5U varies from 70 to 79.9g, affecting the playing style and speed.
Terms Used in Lawn Tennis and Badminton
| Tennis Terms | Badminton Terms |
| Ace | Backhand |
| Advantage | Baseline |
| Baseline | Clear |
| Break Point | Drive |
| Deuce | Drop |
| Double Fault | Feint |
| Forehand | Flick |
| Grand Slam | Footwork |
| Let | Forehand |
| Lob | Hairpin Net Shot |
| Love | Kill |
| Match Point | Let |
| Rally | Lift |
| Serve | Long Serve |
| Smash | Match Point |
| Volley | Net Shot |
| Backhand | Rally |
| Challenger | Serve |
| Crosscourt | Short Serve |
| Drop Shot | Smash |
| Fault | Tumble |
| Game Point | Underhand |
| Half Volley | Flick Serve |
| Overhead | Deception |
| Passing Shot | Crosscourt |
| Return | Fault |
| Seed | Feather |
| Set Point | Game Point |
| Slice | Racket Face |
| Tiebreak | Service Court |
Shuttlecock Vs. Tennis Ball
| Characteristics | Shuttlecock | Tennis Ball |
| Design and Materials | Consist of a console based crock covered with 16 features. | The hollow rubber core is covered with fibrous felt . |
| Aerodynamics and Flight | Design to fly fast but its speed reduces faster than the ball. The features cause more drag and reduce the speed. | Its overall shape keeps its speed maintained. |
| Bounce and Game Dynamics | Shuttlecock does not require a strategic play to keep the shuttle in motion. | Design to bounce which needs different strategies to play as bounce causes different directions. |
| Speed and Scoring | Get higher speed when serving but reduce the speed quickly. Require rapid responses. | Travels on low speed as compared to the starting speed of the shuttle but maintains its momentum. |
| Durability and Usage | Less durable. Features get damaged easily and require more changes in a play. | Very durable. Balls need so few changes in the professional game. |
Conclusion
I have covered a lot of things like important terminologies related to service rules, service rules of badminton and tennis, and comparison between services and scores. There are many other differences between both objects and court size. You can ask me to write about it. If you like my content, please comment and share. I have written useful information about badminton net height and net width that you may read.
